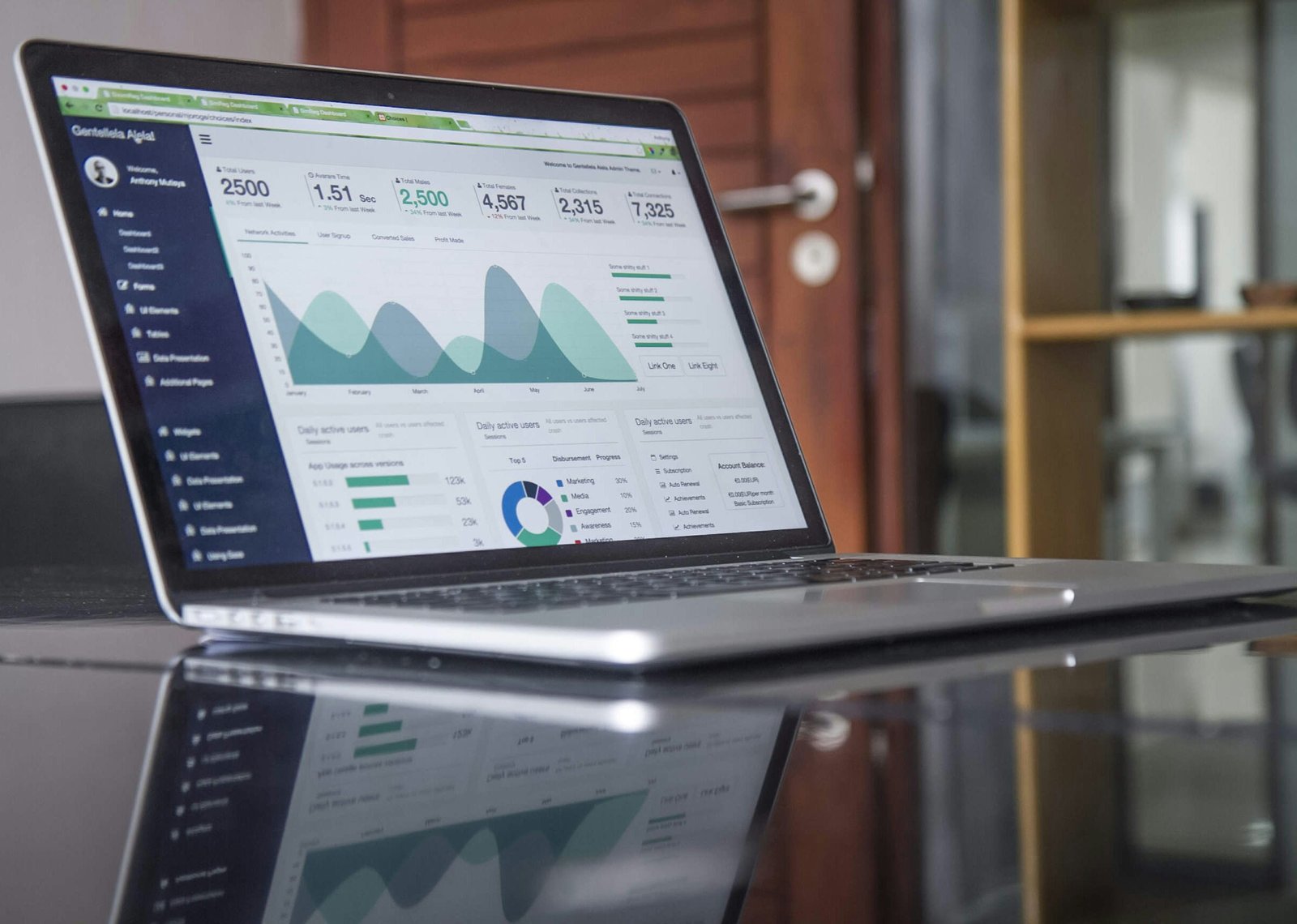
Introduction
Open-source software represents a revolutionary shift in the technology landscape, characterized by the free distribution of source code that allows users to modify, enhance, and distribute software as they see fit. This model has gained remarkable traction in the tech industry, as its advantages become increasingly evident amidst ongoing challenges such as high software costs, rigid licensing agreements, and pervasive vendor lock-in. For organizations relying on proprietary software solutions, these barriers can result in significant operational limitations and expenses.
Within this dynamic environment, open-source software emerges as a viable alternative, mitigating common pain points while promoting innovation and collaboration. Organizations can avoid long-term commitments and costly licensing fees, as many open-source options are available at no cost, thus enabling businesses of all sizes to access sophisticated tools irrespective of their financial standing. Furthermore, the inherent flexibility of open-source projects offers users the opportunity to customize their software solutions to meet specific needs, providing them with greater control over their technological environment.
This blog post will delve into the transformative impact of open-source software, examining key benefits such as enhanced security through community scrutiny, accelerated development cycles, and perpetual support from vibrant user communities. Readers can also expect to encounter compelling real-world success stories showcasing how various organizations have effectively implemented open-source solutions to drive their operations forward. Additionally, we will explore emerging trends in the open-source ecosystem that may influence future software development. By illuminating these aspects, we aim to underscore the significance of open-source software in the modern tech industry and its potential to redefine traditional paradigms.
Understanding Open-Source Software
Open-source software is defined as software that is made available with its source code, allowing users to study, modify, and enhance it. This approach promotes transparency, as anyone can inspect the code for potential security vulnerabilities or performance issues. The key principles behind open-source software include collaboration among developers, which fosters innovation and accelerates improvements. Licensing in this space typically allows for both personal and commercial use, making it an attractive option for organizations worldwide.
Several prominent projects illustrate the impact of open-source software on various industries. Linux, for example, is an open-source operating system that has become the backbone of many servers and computing environments. Its modularity and flexibility have led to widespread adoption in enterprise settings. Similarly, the Apache HTTP Server, an open-source web server software, has played a crucial role in shaping the internet, powering a significant portion of websites globally.
WordPress is another notable example, revolutionizing content management systems by allowing users to create and manage their own websites with ease. With over 40% of the web built on its platform, WordPress’s open-source nature has empowered countless individuals and businesses to establish an online presence without significant financial barriers. The open-source market is witnessing significant growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% in the coming years.
Statistics indicate that open-source software is increasingly being adopted by enterprises; for instance, as of 2023, approximately 90% of organizations utilize open-source solutions. This shift reflects a growing recognition of the advantages offered by community-driven projects, including cost savings, flexibility, and a wider pool of talent contributing to development. These factors combined are transforming not just technology practices, but also business models across various sectors.
The Benefits of Open-Source Software
Open-source software (OSS) provides numerous advantages that are increasingly attracting businesses and developers alike. One of the most compelling benefits is its cost-effectiveness. Unlike proprietary software, which often comes with hefty licensing fees, OSS is typically available for free, allowing organizations to significantly reduce their operational expenses. This financial flexibility is particularly advantageous for startups and small enterprises that may operate on limited budgets.
Moreover, open-source software offers unparalleled flexibility and customization options. Users can modify the source code to tailor applications precisely to their needs, thereby enhancing functionality and aligning with business objectives. This level of adaptability is particularly crucial in today’s rapidly changing technological landscape. For instance, a company specializing in e-commerce could modify an open-source content management system to incorporate unique features that cater to its target market, thereby gaining a competitive edge.
Security is another notable benefit of open-source software. As OSS provides access to the source code, developers worldwide can scrutinize it for vulnerabilities and contribute fixes. This collaborative approach can lead to a more secure software infrastructure, as was demonstrated in the case of the Linux operating system. Major corporations have successfully implemented OSS solutions, leading to increased efficiency and innovation. For example, Mozilla Firefox, an open-source web browser, demonstrates how community-driven development can yield a robust and secure product.
Research has shown that companies adopting open-source solutions can experience not only reduced costs but also faster time-to-market for new features. In summary, the advantages of open-source software—in terms of affordability, flexibility, customization, and enhanced security—underscore its transformative potential in the software industry. By embracing OSS, businesses can foster innovation while maintaining a sustainable operating model.
Future Trends in Open-Source Software
The landscape of open-source software is rapidly evolving, driven by several key trends that are shaping its future. One significant trend is the integration of open-source solutions with cloud computing. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud technologies, open-source platforms have become essential in deploying scalable, flexible, and cost-effective applications. The combination of open-source software with cloud infrastructure enables businesses to leverage collaborative tools and services, fostering innovation and optimizing resource allocation.
Another area witnessing substantial growth is the intersection of open-source with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Open-source libraries and frameworks, such as TensorFlow and PyTorch, have democratized access to advanced AI technologies. This has empowered developers and researchers to experiment, innovate, and share their findings, accelerating advancements in machine learning applications across various industries—from healthcare to finance. As AI becomes increasingly embedded within software solutions, the reliance on open-source projects is likely to expand, reinforcing their role in fostering collaboration and knowledge sharing.
In addition to these technological advancements, community-led initiatives are playing a pivotal role in the evolution of open-source software. The collective efforts of diverse contributors enable transparency, inclusivity, and continuous improvement within the software development process. However, this model also presents challenges, such as sustaining community engagement and ensuring that contributions maintain high-quality standards. Addressing these challenges may involve employing structured governance models and creating pathways for onboarding new contributors, thereby bolstering community resilience.
In conclusion, the future of open-source software is primed for growth, driven by cloud integration, AI advancements, and strong community involvement. By embracing these trends, organizations and individual developers can contribute to and shape the ever-transcending position of open-source software within the technology landscape.